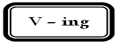“UNIT
2 - TOEFL STRUCTURE”
The
main points in the TOEFL Structure that should be considered in the groups by
way of finding out where the Subject, Verb, Object, and Adverb. Of the four,
the most important is to be known as Subject and Verb, because it eliminates
most of the TOEFL Subject and verb of the sentence to be analyzed or ask
questions.
1. Passive Voice
Passive Voice is one of the few patterns
that exist in the English language that has meaning (-in) in its use.
Simple
Present:
·
Active:
Someone repairs the bicycle
·
Passive:
The bicycle is repaired by someone
Present
continuous:
·
Active:
Someone is repairing the bicycle
·
Passive:
The bicycle is being repaired by someone
Present
Perfect:
·
Active:
Someone has repaired the bicycle
·
Passive:
The bicycle has been repaired by someone
Past
simple:
·
Active:
Did john eat the food?
·
Passive:
Was the food eaten by John?
Past Continues:
·
Active:
Someone was repairing my bicycle when I arrived home
·
Passive:
The bicycle was being repaired by someone when I arrived home
Past
perfect:
·
Active:
Someone had repaired the bicycle
·
Passive:
The bicycle had been repaired by someone
Modal
·
Active:
Someone will repair the bicycle
·
Passive:
The bicycle will be repaired by someone
EXERCISE FOR
PASSIVE VOICE
Someone can’t repair the bicycle
The passive form of
the above sentence is: The bicycle can’t by someone.
(a) Be repaired (c) have to be repaired
(b)
Repaired (d)
is being repaired
2. Participle
A.
Active Participle
Active
participle is a verb that ends - ing as having, pointing, walking, etc. Active
participle often appears after the object of the verb: see, hear, smell, feel,
watch, notice, listen to, look at, observe, keep, find, catch, leave, which
serves as an adjective or adverb:
Example
: I felt the house shaking
I saw the boat sinking
He
notice me leaving the house
B.
Passive Participle
Passive
participle is a verb form to - 3. If the past participle to be preceded by a
passive form there arose pattern:
Example
: A table is made of wood
I
was born in July, etc
EXERCISE FOR PARTICIPLE
Having developed a new method in medicine, the doctor was invited to give a
speech in a seminar. The underlined words means:
(a) because the doctor was developing a new
method in medicine
(b) after the
doctor had developed a new method in medicine
(c) although the doctor developed a new
method in medicine
(d) the doctor was developing a new method in
medicine
3.
Concord
Concord
or agreement is a rapprochement between the subjects in a sentence with a verb/it’s
auxiliary.
A.
Subject sentences in the singular preceded by the
words: every...., each of, neither of..., one of…
Example:
The school has a lot of classrooms; each
of them is equipped with an overhead projector.
Ø
Each
of the participants
has received an invitation
Ø
Everyone
likes her
Ø
The
actress, along with
her manager and some friends, is going to a party.
B.
Subject sentences in the plural which is arranged by...
and... Or both... and…
Example: A red Honda and blue ford are
parked outside
Both elephant and tiger are becoming extinct.
EXERCISE FOR CONCORD
Each the
participants received an invitation.
(a) to, is (c)
of, is
(b)
of, has (d)
of, were
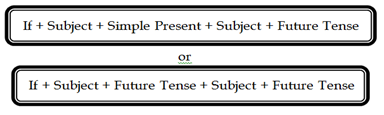
4. Conditional Sentence
Conditional
Sentences are sentences that express an expectation or picture in the form of conditional
sentence.
A. Probable
condition, is that something will probably happen in the future when the time
comes and now filled.
Example: If Betha comes, I will give her the
message
He will not go to the picnic if it
rains
B.
Improbable condition, is that the incident is contrary
to the truth, because it is imaginary (Contrary to fact).
Example: If I were rich I would give my money to
the poor
If he smoked less, he wouldn’t cough so much
C.
Impossible condition, which describes an event as opposed
to in the past and there is no hope will happen.
Example: If I had known her number, I would have
called her.
She could have finished the exam, if
she had had more time
EXERCISE FOR
CONDITIONAL SENTENCE
If I prepared the lesson, I good mark.
(a) Will
get (c)
would get
(b) Would
have got (e) had got
5. Causative
Causative sentence is stating that other
people who do the work for the subject sentence.
EXERCISE FOR CAUSATIVE
Do you have your
windows cleaned every month?
I didn’t have them yesterday.
(a) Cleaning (c) the Clean
(b) Clean (d) cleaned
6. Relative Pronoun
Relative
Pronoun is a word used to replace one of the main parts of a sentence or other
sentence that connects the two sentences into one compound sentence (sentence
complex). The words that are used as a link is: Who, Whom, Whose, Where, When.
Exercise for Relative Pronoun
The man wrote about the explosion was an eyewitness.
(a) Whose (c)
Which
(b) Whom (d) Who
7. Negative – Either Neither
Either
or neither is used to incorporate negative sentences.
Example: - They do not come late
- Brian does not come late
>>
They do not come late and Brian does not either / neither does Brian
A.
Gabungan Berlawanan Setara
Combined use of opposite use of
conjunctions but/while.
Example: - We do not have to return the book
tomorrow
- He has to return the book
tomorrow
>> We do not have to
return the book tomorrow, but/ while he does
B.
Gabungan Setara
Whenever the word “either” and “Neither” followed by
“or” and “nor” the verb/auxiliary its possible singular or plural depends on
the word after “or” or “nor” whether singular or plural.
Example:
Neither
John nor Bill is going to class
today
Either John or Bill is going to the beach today.
The
phrase “not only” ... but also ... “or” ... as well as ... “also connects the
use of equivalent type and form of the word.
Example:
They got not only modal but also
money.
Beth
plays guitars as well as violin.
Exercise for Negative
I didn’t not like the food and sultan did .
(a) Not neither (b)
Not either
(b) Neither (d) either
8. Question Tag
Question tags are questions tailed whose
function is to reinforce a statement. Could be interpreted as a “right?”
Exercise for Question
Tag
They do not want to join us, ?
(a) Do they (c) did they
(b) Don’t they (d)
does they
9. Conjunction
Exercise for Conjunction
There is fog on Chicago , the place has been diverted.
(a) So (c)
Whereas
(b)
Therefore (d)
Otherwise
10. Gerund
Can
be used as subject, object, complement, after prepositions, after certain verbs
(Stop, Finish, dread, like, Prevent, deny, collect, delay, postpone, enjoy,
stand and etc), and the compound (A reading book, a swimming pool, a diving
board).
Exercise for Gerund
I will finish my work within 2 hours.
(a) Do it (c)
does
(b) Do (d) doing
11. To infinitive
To
infinitive is a verb form that accompanied the first “to” with some of the
rules to use the infinitive is as follows.
Example: My
father promised to buy me a new jacket
Alice plans to visit her uncle this weekend
It seems to be good
A. Adjective
Example: He was unable to come on
time this morning
It is very hard to believe
that he is one of the suspects of the bank robbery.
B.
After Object Accusative
Example: They
get us to clean the cars
Mr.
Benson asked peter to bring his laptop to his room
C. After
Question Word
Example: We know how to operate the machine
You do not
know what to, so please shut up!!
Exercise for To infinitive
Alice to visit her
uncle this weekend.
(a) Plans (c)
to plan
(b) Plan (d) to plans